HOSPITAL INFECTION CONTROL (HIC)
HOW TO CONTROL HOSPITAL INFECTION
The term infection is generally used to mean the deposition and multiplication of bacteria and other micro-organism in tissues or on surface of the body where they can cause adverse effect .
Hospital infection means infection acquired by patients while they are in the hospital, or by memebers of hospital staff , the term hospital acquired infection is sometimes used .This may be associated with sepsis or other form of infective illness ,either in hospital or after the patient returnes home ,cross -infection means infection acquired in hospital from others people either patient or staff. self or endogenous infection means infection caused by microbes which the patient carries on normal or septic areas of his own body ,including organism which these areas have aquired in hospital .
NOSOCOMIAL INFECTION = Nosocomial infection is the most common adverse event experienced by hospitalized patients: more recent data suggest that 10% of patient develop a nosocomial infection that is caused by hospital . during admission to an acute care hospital ,Hospital acquired infection increase Morbidity ,extend hospital says ,and increase hospital charges ,They also are associated with substanial increase in hospital Moratality .Analysis of discharge data from more than 5 million pediatric hospitalization revealed that ” Postoperative sepsis” And infection as a result .
Effective infection prevention and control to proving high quality healthcare for patients and a safe working environment for those who work in healthcare settings . It is important to minimize the risk of spread of infection to patients and staff in hospitals by implementing good infection control programme .
The following steps how to hospital infection control policies are needed to be framed and practiced and monitored by the Hospital Infection control Team( HICT) & Hospital infection control committee ( HICC) .
- 1. Guidelines for preservation & control of infections
- 2- Antimicrobial policy
- 3- Surveillance policy
- 4- Disinfection policy
- 5- Isolation policy
- 6- Policy for investigation of an outbreak of infection
- The overall aim of this document is to provide evidence based information in the prevention and control of hospital infection. it is relevant to all doctors, nurses, other clinical professionals and managers those working in hospitals .
AIM OF HOSPITAL INFECTION CONTROL
The NABH Hospital Infection control (HIC) Chapters aims; at; 1- Effective Infection Control Programme . 2-Reducing / Eliminating infection risk to patients , visitors and providers of care . 3- Measures and action taken to prevent or reduce the risk of hospital Acquired Infection. 4- Action plan to Control Outbreaks.
INFECTION PREVENTION PRACTICES
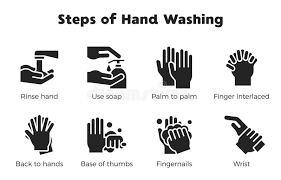
- Hand Hygiene .
- PPE( PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT)
- Prevention of Needlestick Injury and Injury From other Sharp Items
- Pre and Post exposure prophylaxis
- Environmental Cleaning
- Patient care Equipment Cleaning
- Linen And Laundry Management
- Safe Disposal of Biomedical Waste ( BMW ) .

STANDARD PRECEAUTION
The Infection Prevention Practice that apply to all patients ,regardless of suspected or confirmed infection status ,in any setting in which Health care is Delivered are called Standard Precaution .
Standard Precaution are the Work Practice Required to Achieve a basic level of infection prevention and control. Transmission – Based Precaution are used when Standard Precaution alone are not Sufficient to Prevent the spread of infectious agent . Transmission – Based Precaution are Based upon the mode of transmission of the infectious agent .

HIC 1: The Hospital has an infection control manual ,which is periodically updated and conducts surveillance activities.
- HIC1a- it focuses on adherence to standard precautions at all times.
- HIC1b – Cleanliness and general hygiene of facilities will be maintained and monitored .
- HIC1c: – cleaning and disinfection practice are defined and monitored as appropriate .
- HIC1d- Equipment cleaning ,disinfection and sterilisation practice are included.
- HIC1e- Laundry and linen management process are included.
HIC 2: The Hospital takes actions to Prevent or reduce the risks of hospital associated infections (HAI) in patients & Employees.
- HIC2a- Hand Hygiene facilities in all patient care areas are accessible to health care providers
- HIC2b- Adequate gloves, masks, soaps, and disinfectants are available and used correctly.
- HIC2c- Appropriate pre and post exposure prophylaxis is provided to all concerned staff members.
COMMON HOSPITAL INFECTION
1- UTI: Urinary Tract Infections; 2- SSI: Surgical Site Infections; 3-BSI: Blood Stream Infections; 4-GI: Gastrointestinal Infections 5-VAP: Ventilator associated pneumonia 5- CLABSI: Central line associated Bloodstream Infections 6-HAI: Healthcare Acquired Infection;
Technology and Innovation in Hospital Infection Control
The improvement of hospital infection control has been greatly aided by technology and innovation , here are some example of how technology and innovation are being used in hospital infection control.
1- Ultraviolet (UV) Disinfection system UV light killed bacteria and viruses by UV radiation .UV disinfection system are being used in hospitals to disinfect patient rooms, and operating rooms and other areas where infectious organism may be present . these system use UV lamps to reduce the risk of HAI.
2- Electronic Hand Hygiene Monitoring One of the best strategies to stop the spread of infection in hospitals is to practice good hand hygiene . EHHM system use sensors to track when healthcare person enter and exit patient room , & can track their hand washing system.

3- Antimicrobial Surface In hospitals ,bed rails and door knobs are two frequently touched items and can host bacteria and viruses , antimicrobial surface are created to eliminate virus and bacteria .
4- Advanced Air Filtration System In healthcare facilities ,particularly in areas such as operating rooms and intensive care units ,infection spreads through the air . modern air filtration system are capable of removing germs and viruses, as well as other airborne particles.
5- Electronic Patient Monitoring Using EPM system to track vital signs and other medical data ,healthcare professionals can identify patients who could be at risk of infection. when a patient condition change ,these system can notify appropriate healthcare professionals allowing earlier intervention& possibly reducing the risk of infection.

Challenges in Implementing effective Hospital Infection control
HCWs often resist adopting new infection control protocols due to their familiarity with new existing practice ,the shift to new methods can be met with reluctance or hesitancy , stemming from the comfort and habituation to established procedures . embracing change in healthcare settings can be challenging and requires extensive training and support mechanism .
1 LACK OF RESOURCES-– Adequate resources such as PPE , cleaning materials , finance and educated employees ,are all required for effective infection control . in the absence of these resources, implementing and maintaining effective infection control may be difficult .
2 -RESISTANCE TO CHANGE – HCWs may be resistant to change and new protocols ,they ,may be used to certain practice and find it difficult to adopt new infection control measure.
3- HIGH PATIENT TURNOVER– Hospitals are busy places with lots of people entering and existing .due to this ,keeping a hygienic and clean workplace may be challenging.
4- VARIABILITY IN PATIENT CONDITIONS – Patients may need various infection control strategies according to their various medical problems implementing a common infection control technique may be difficult due to this variation.
5- LIMITED COMMUNICATION AND COLLABRATION– Effective communication and collaboration among medical staff ,patients ,and patients relatives are essential for effective infection control .this could be challenging in a hospital setting with several department and personal.
6- INADEQUATE TRAINING – Healthcare personal may not have sufficient training methods for preventing infections .They may not be able to execute effective steps to prevent infectious without the right training.
7- PATIENT BEHAVIOUR– Infection control measure such as hand hygiene and isolation measure ,might increase the possibility of an infection spreading.

The Future Of Hospital Infection Control
Hospitals are leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) & Machine learning (ML) to proactively identify and curb the spread of infection , these technology can detect patterns and predict potential outbreaks , AI- powered system monitor staff compliance with hand hygiene regulation and identify infection on surfaces, alerting staff for timely intervention.

TRENDS AND OPPORTUNITIES 1- USES OF AI AND ML 2- IMPLEMENTATION OF TELEMEDICINE 3- ADVANCE DISINFECTION TECHNOLOGIES 4- INTEGRATION OF ENVIORMENTAL MONITORING 5- INCREASED FOCOUS ON ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP 6- INTEGRATION OF INFEFCTION CONTROL INTO PATIENT SAFETY PROGRAMMS 7- INCREASED COLLABORATION BETWEEN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES 8- PATIENT INVOLVEMENT
Telemedicine has emerged as a vital tool in infection control ,enabling remote consultation and monitoring healthcare professionals can receive training and education on infection control prevention techniques. remotely ,reducing the risk of transmission within healthcare settings . Recognizing the importance of patient involvement in infection control hospitals are educating and engaging patient in their care, empowering patient with knowledge about infection prevention methods contributes significantly to reducing HAIs possible trends and opportunities may influence hospital infection control in the future .
INFECTION CONTROL – A PROBLEM FOR PATIENT SAFETY
Nosocomial or hospital acquired ,infections are today by far the most common complication affecting hospitalized patients ,indeed the harward medical practice study found that a single type of nosocomial infection- surgical wound infection- constitueted the second largest category of adverse events ,long considered the greatest risk that the hospital enviorment poses to patients .
since then the study and control of nosocomial infection have been profoundly shaped by the discipline of public health ,with its emphasis on survillience and epidemiologic methods,These infection are not only the most common types of adverse events in health care ,they may also be most studied .
patient safety has emerged as an important health care issues because of the consequences of iatrogenic injuries , : preventable injuries result largely from system failures,not from individual inadequacy. Human factors research in nonmedical settings suggest that people tend to take the path of least effort : hence demanding greater vigilence from providers of medical care may not result in meaningful safety improvement ,instead ,redesigning faulty system appears to be a more promising way to reduce human error .
MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS IN INFECTION CONTROL
Infection control activities are facing new challanges,but the resources dedicated to infection control are too frequently insufficient. The challanges to infection control in 21st century are huge .The evolution rewards benchmarking .Lack of reimbursement for specific healthcare associate infection( HAIs) .
- organizational aspects and infection control staff
- Training and accreditation of infection control professionals
- structural requirements
- ward staffing
- microbiological support.
